Reddy Update: Difference between revisions
From IntRoLab
| Line 151: | Line 151: | ||
== Motor Controller Variables == | == Motor Controller Variables == | ||
<pre> | |||
typedef struct _SharedVariables | |||
{ | |||
union { | |||
struct { | |||
unsigned char CtrlMode; | |||
unsigned char CtrlType; | |||
unsigned char SetPointSource; | |||
unsigned char PosMesSource; | |||
unsigned short ErrorCode; | |||
short SetPoint; | |||
short SetPointMax; //Maximum SetPoint | |||
short SetPointMin; //Minimum SetPoint | |||
short Current; | |||
short CurrentOffset; | |||
short ADCValue; | |||
short ADCOffset; | |||
short ICValue; | |||
short ICOffset; | |||
short ThermalState; | |||
//CONTROL VARIABLES | |||
short Speed;//16 bit speed | |||
short Position; //16 bits position | |||
short Acceleration; | |||
//PID REF AND MES POINT | |||
short RefPoint; | |||
short MesPoint; | |||
float pid_kp; | |||
float pid_ki; | |||
float pid_kd; | |||
float pid_error; | |||
float pid_error_accum; | |||
float pid_error_derivative; | |||
float pid_error_accum_max; //PID I value max limit (abs) | |||
short PIDOut; | |||
//RAM LOC7 (PID + TRAPZ VARIABLES) | |||
short SpeedMax; //for Trapz | |||
short AccelerationStep; //for Trapz, Speed | |||
//RAM LOC8 (TRAPZ VARIABLES) | |||
short InitPoint; //for Trapz | |||
short DestPoint; //for Trapz | |||
short NextPoint; //for Trapz | |||
//RAM LOC9 (CURRENT LIMIT) | |||
short CurrentLimit; //unit = mA | |||
short PWM_CurrentLimit; | |||
short PWM_CurrentStep; //PWM increment | |||
unsigned char CurrentLimitActive; | |||
unsigned char EncoderBias; //Setting this to 1 will invert the encoder sign | |||
unsigned char MotorBias; //Setting this to 1 will invert motor polarity | |||
unsigned char padding[3]; | |||
} __attribute__((packed)); | |||
unsigned char m_data[]; | |||
}; | |||
} SharedVariables; | |||
typedef struct _GlobalVariables | |||
{ | |||
union { | |||
struct { | |||
//All control variables | |||
SharedVariables m_variables[4]; | |||
//additional (global) variables | |||
unsigned char m_ESTOPEnabled; | |||
unsigned char m_WriteEEPROM; | |||
short m_loopTime; | |||
unsigned char m_padding[4]; | |||
} __attribute__((packed)); | |||
unsigned char m_data[]; | |||
};//union | |||
} GlobalVariables; | |||
</pre> | |||
== Useful Examples == | == Useful Examples == | ||
Revision as of 15:06, 28 July 2009
Schedule
| Week 31, July 27 - August 1 |
|
| Week 32, August 3 - August 9 |
|
| Week 33, August 10 - August 15 |
|
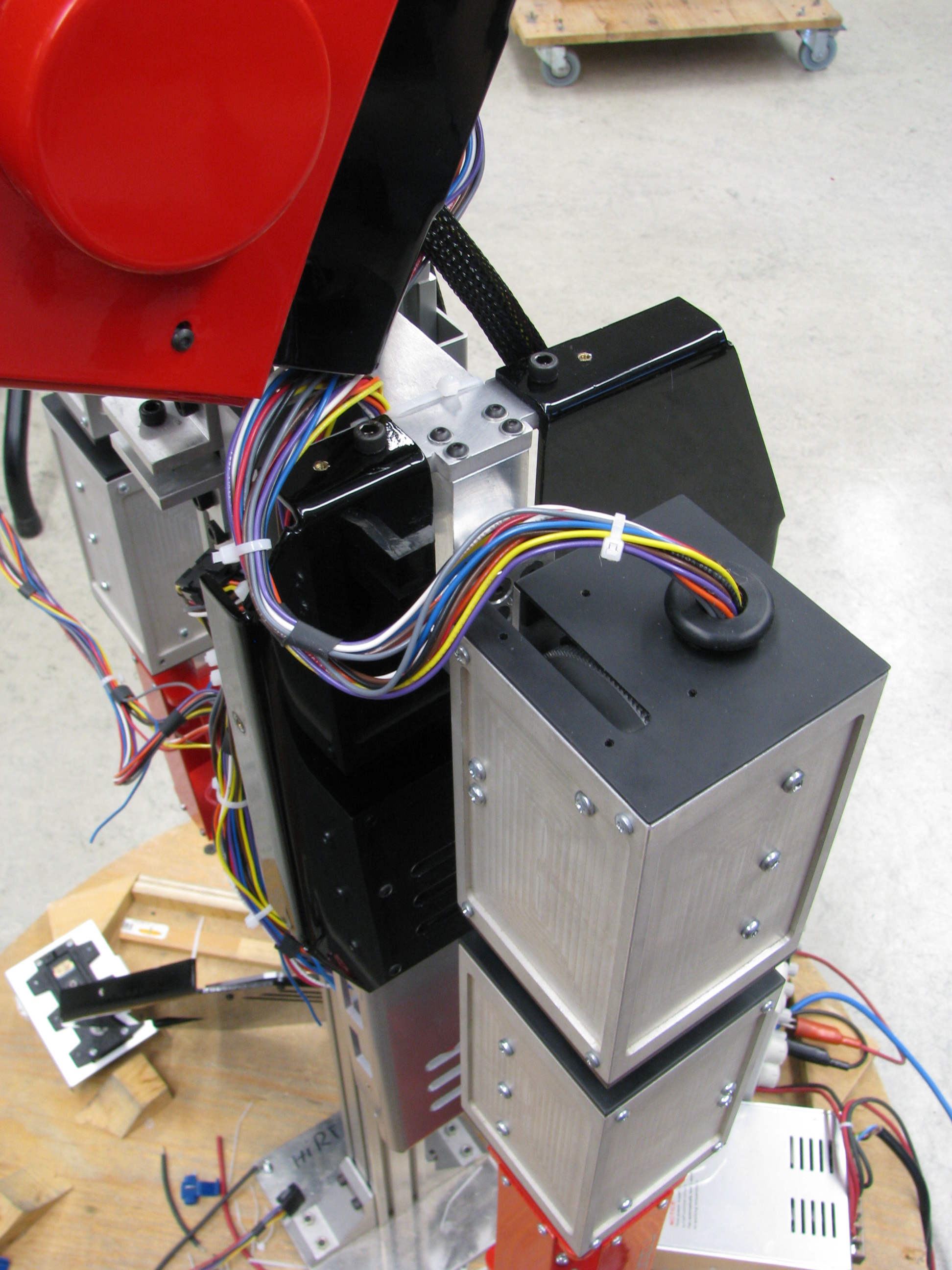
Arm Improvements
To have better control of the arm (and neck) motors, we did the following :
- Change the Motor PCB to support
- Temperature detector. A signal will be sent to the motor controller if the motor temperature is higher than 60 degrees celcius. Analog temperature value is also available.
- Potentiometer feedback.
- Motor power connection.
- Design a new PCB with support to 4 motors
- Communicate with the CAN bus already available on Reddy
- Allow position feedback from the RS-232 interface
- Create a tuning GUI for easier setup of the robot controllers
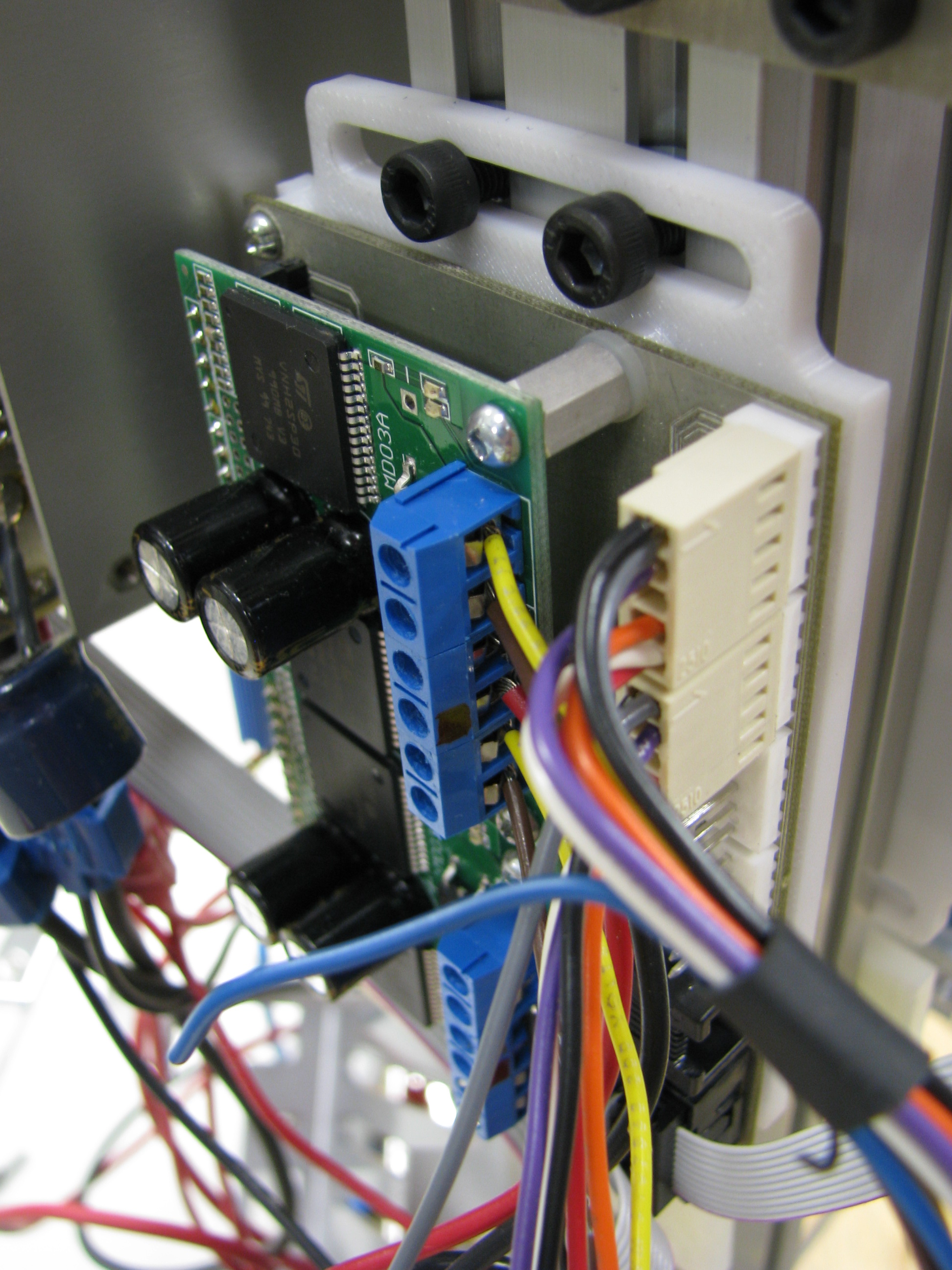
Motor PCB
Motor Controllers
- A new motor drive that can connect up to 4 motors have been designed.
- A new adjustable bracket for fixing the drive to the side of the robot have been designed.
- We installed two motor controllers (one on each side) to allow the modification of 8 motors. Motors modified are :
- Arm-elbow (x2)
- Arm-shoulder (x2)
- Arm-updown (x2)
- Neck-YES (x1)
- Neck-NO (x1)
Cabling Improvements
- Cables are now better organized
- Added connectors inside the arm to disconnect motors easily for repairs
- Signals are color coded as follow (TODO ADD DOCUMENTATION)
- Red
- Green
- Black
- Yellow
- Purple
- Gray
- White
- Blue
Head Improvements
File:ReddyGravityCompensation.jpg
Motor controllers for head movement (YES-NO)
- Same motor controllers were used for the neck to add overheating protection and better feedback / control
- Internal servo potentiometers were used for position control.
Tuning the motor controller
A GUI was created to facilitate motor tuning.
RS-232 protocol enhancements
- We added a CAN command to the RS-232 robot interface to allow direct communication with the motor controllers. The RS-232 robot interface now acts as a RS-232 to CAN bridge and bidirectional communication is now possible. This will allow feedback from the motor controllers (current, position, speed, etc.)
(RS-232 CAN COMMAND) <------------------------> (MOTOR DRIVE CAN INTERFACE)
CAN command format for RS-232 communication
Serial messages containing CAN commands will have the following stucture :
| HEADER | CAN_MSG_PRI_MSB_CMD | CAN_MSG_TYPE | CAN_MSG_BOOT_RTR_LENGTH | CAN_MSG_CMD | CAN_MSG_DEST | CAN_MSG_DATA |
| (3 bytes) | (1 byte) | (1 byte) | (1 byte) | (1 byte) | (1 byte) | (8 bytes) |
|
|
|
|
if (MSG_TYPE == REQUEST)
endif if (MSG_TYPE == SENSOR_HIGH_PRIORITY)
endif |
|
|
Note: It is not essential to understand the structure of the CAN messages. Souce code will be provided to format the data correctly.
Motor Controller Variables
typedef struct _SharedVariables
{
union {
struct {
unsigned char CtrlMode;
unsigned char CtrlType;
unsigned char SetPointSource;
unsigned char PosMesSource;
unsigned short ErrorCode;
short SetPoint;
short SetPointMax; //Maximum SetPoint
short SetPointMin; //Minimum SetPoint
short Current;
short CurrentOffset;
short ADCValue;
short ADCOffset;
short ICValue;
short ICOffset;
short ThermalState;
//CONTROL VARIABLES
short Speed;//16 bit speed
short Position; //16 bits position
short Acceleration;
//PID REF AND MES POINT
short RefPoint;
short MesPoint;
float pid_kp;
float pid_ki;
float pid_kd;
float pid_error;
float pid_error_accum;
float pid_error_derivative;
float pid_error_accum_max; //PID I value max limit (abs)
short PIDOut;
//RAM LOC7 (PID + TRAPZ VARIABLES)
short SpeedMax; //for Trapz
short AccelerationStep; //for Trapz, Speed
//RAM LOC8 (TRAPZ VARIABLES)
short InitPoint; //for Trapz
short DestPoint; //for Trapz
short NextPoint; //for Trapz
//RAM LOC9 (CURRENT LIMIT)
short CurrentLimit; //unit = mA
short PWM_CurrentLimit;
short PWM_CurrentStep; //PWM increment
unsigned char CurrentLimitActive;
unsigned char EncoderBias; //Setting this to 1 will invert the encoder sign
unsigned char MotorBias; //Setting this to 1 will invert motor polarity
unsigned char padding[3];
} __attribute__((packed));
unsigned char m_data[];
};
} SharedVariables;
typedef struct _GlobalVariables
{
union {
struct {
//All control variables
SharedVariables m_variables[4];
//additional (global) variables
unsigned char m_ESTOPEnabled;
unsigned char m_WriteEEPROM;
short m_loopTime;
unsigned char m_padding[4];
} __attribute__((packed));
unsigned char m_data[];
};//union
} GlobalVariables;
Useful Examples
Read all motor positions from the motor controller
Write the SetPoint of motor [0-3]
Future Improvements
- Single 12V power supply could be useful for direct connection to Pioneer robots. A 12V-->8.5V DC-DC (100W) converter is required for this operation. This item can be ordered at Vicor. 8.5V batteries would then be useless.